Timeless inventions
12 amazing American patents that shaped technology and culture

Image: Markus Winkler
The United States Patent and Trademark Office has issued over 12 million patents since its establishment in 1836. Many of the inventors who applied for these patents are well known—such as Elisha Graves Otis or Orville and Wilbur Wright —while others may come as a complete surprise, like President Abraham Lincoln . Some of the patents listed in this article are grandiose; others are smaller and seemingly insignificant. However, they all have something in common: they were invented in our country and changed the course of history. Wondering what they might be? Read on to find out!
1
Locomotive steam-engine for rail (Patent #1)
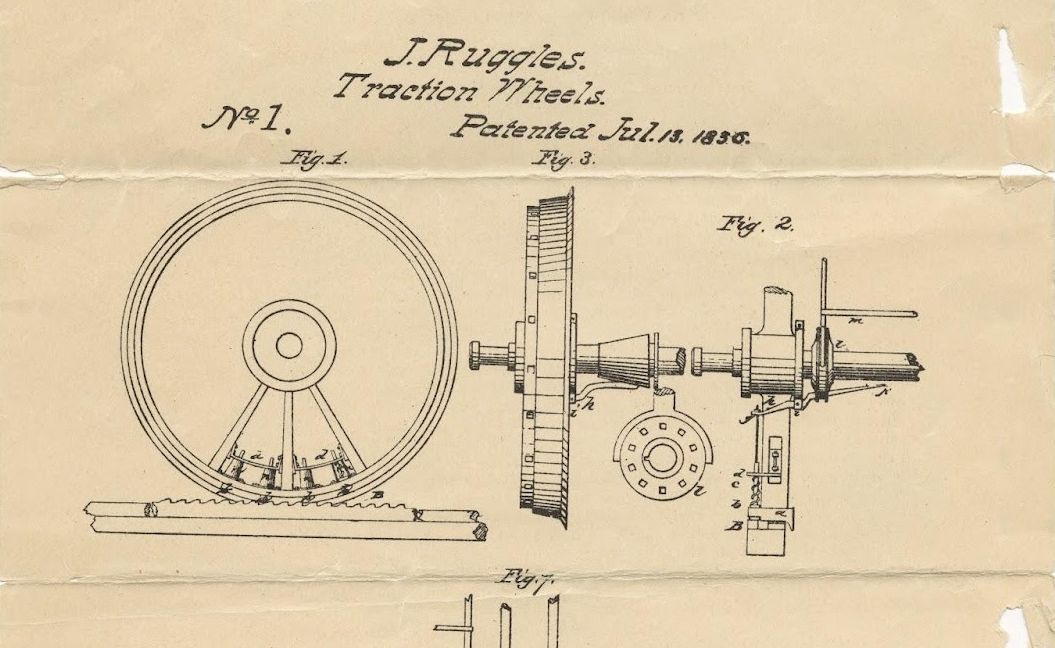
Image: National Archives at College Park - Textual Reference, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Between 1790 and 1836, the United States granted 9,802 patents that were not awarded on their merits and didn’t have an identification number. The Patent Act of 1836, which established the official Patent Office, aimed to make the system more transparent. Among other reforms, it introduced a numbering system for easier identification.
This system started on July 13, 1836, and remains in effect today. United States Patent No. 1 was issued to John Ruggles —an inventor, attorney, and senator from Maine—for improvements in locomotive traction.
2
Anesthesia (Patent #4,848)
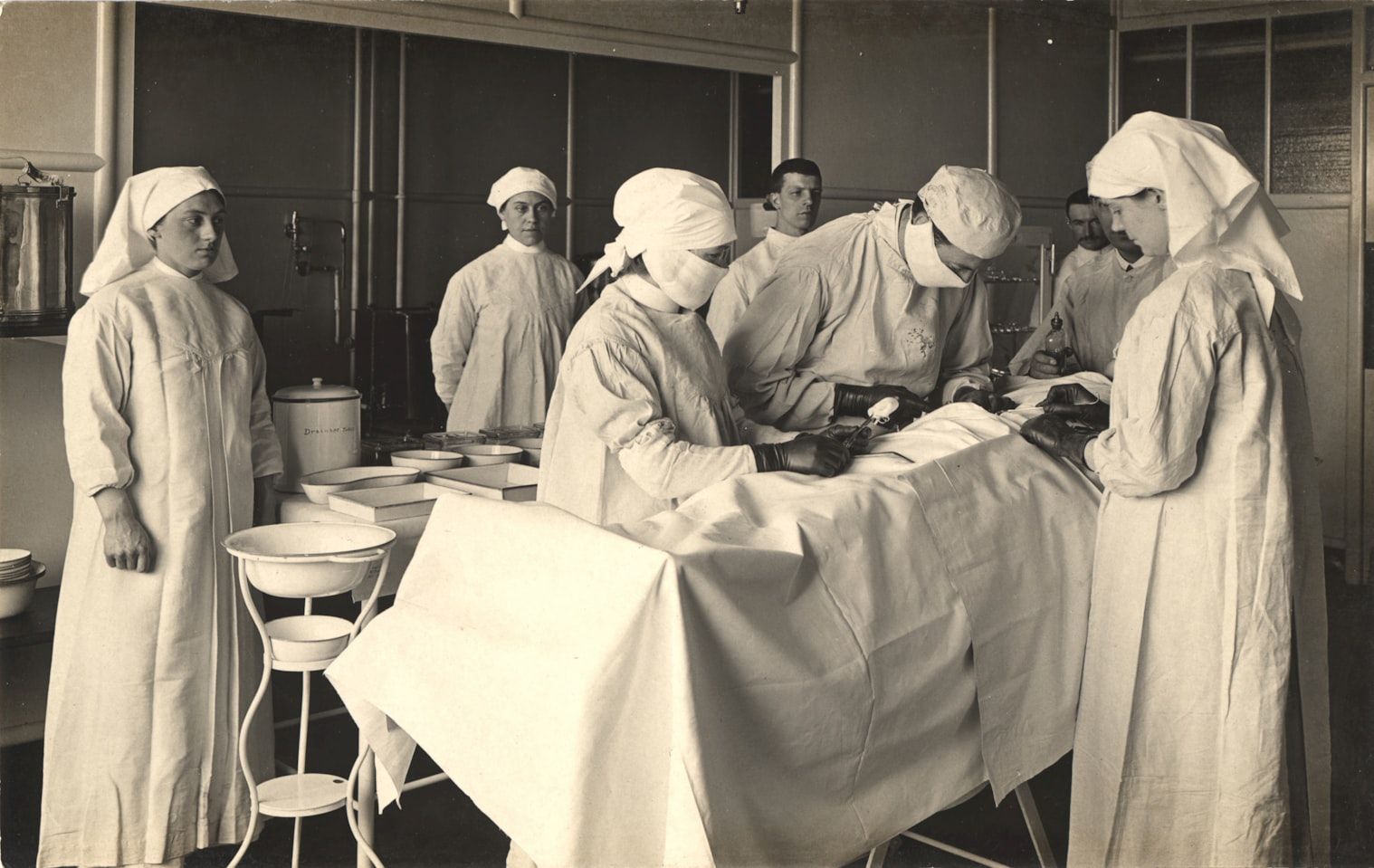
Image: National Library of Medicine
How did patients endure surgery before anesthesia? Before the discovery of an effective anesthetic, surgery was synonymous with excruciating pain. Many large hospitals placed their operating rooms in isolated and remote sections of the hospitals so patients’ screams couldn’t be heard. Alcohol, opium, and even hypnotism were tried as methods of pain relief, but these had little effect.
Fortunately, we no longer have to endure such experiences, thanks to a Boston dentist named William T. G. Morton, who—along with Charles T. Jackson—received the first United States patent for an anesthetic in November 1846.
3
Buoying vessels over shoals (Patent #6,469)
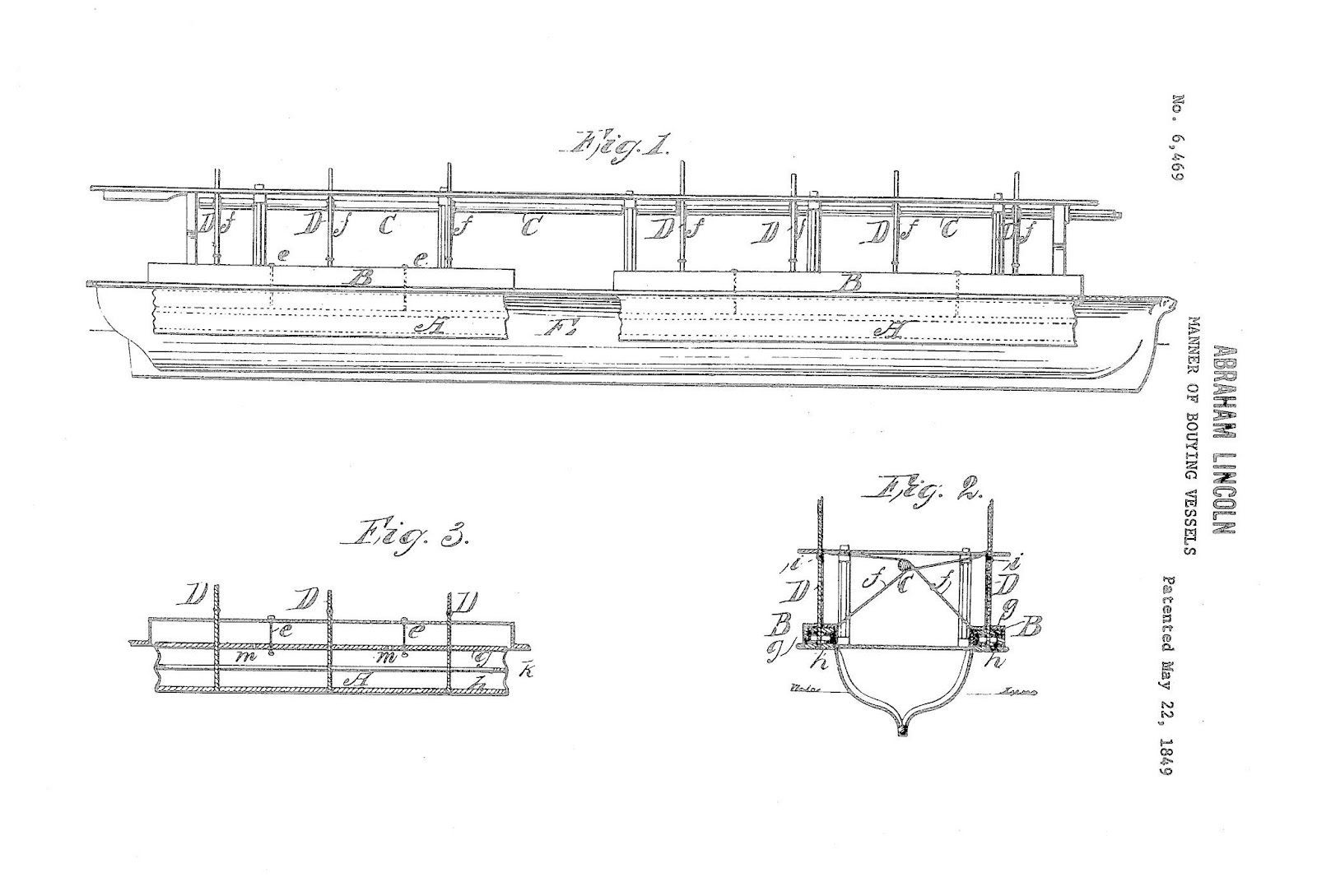
Image: invented by Abraham Lincoln. Issued by United States government Patent Office, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
This may be the most unique patent ever issued by the United States Patent Office: it is the first and only U.S. patent granted to an inventor who later became president. Although at least three presidents—George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, and Abraham Lincoln—were inventors, Lincoln is the only one who formally applied for and received a patent .
In 1849, he was awarded Patent No. 6,469 for a flotation device designed to lift boats over shoals and other obstacles in the water. While the invention itself had little bearing on his election, Lincoln’s inventive mindset and mechanical curiosity served him well during his presidency. Although the device was never commercially produced, his appreciation for innovation helped shape the nation's future.
4
Beehive (Patent #9,300)
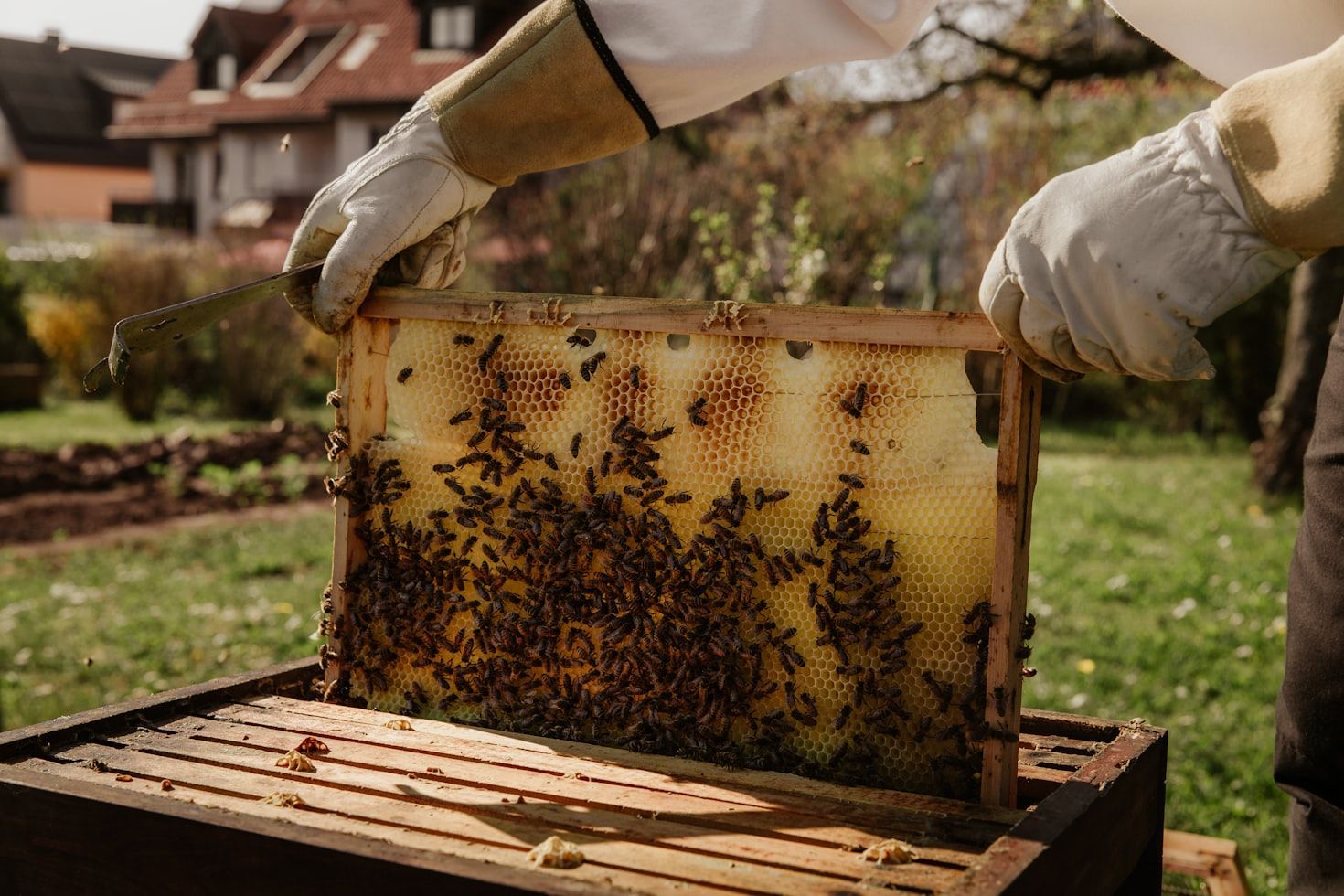

Image: Bianca Ackermann
Beekeeping arrived in America with the early settlers, and by the end of the 18th century, bee colonies were widespread. However, early efforts met with only partial success.
The first U.S. patent for a practical and effective movable-frame beehive—which revolutionized traditional methods of beekeeping—was granted to American apiarist, clergyman, and teacher Lorenzo Lorraine Langstroth on October 5, 1852. His invention of the "bee space" laid the foundation for all modern beekeeping and hive management.
5
Elevator (Patent #31,128)
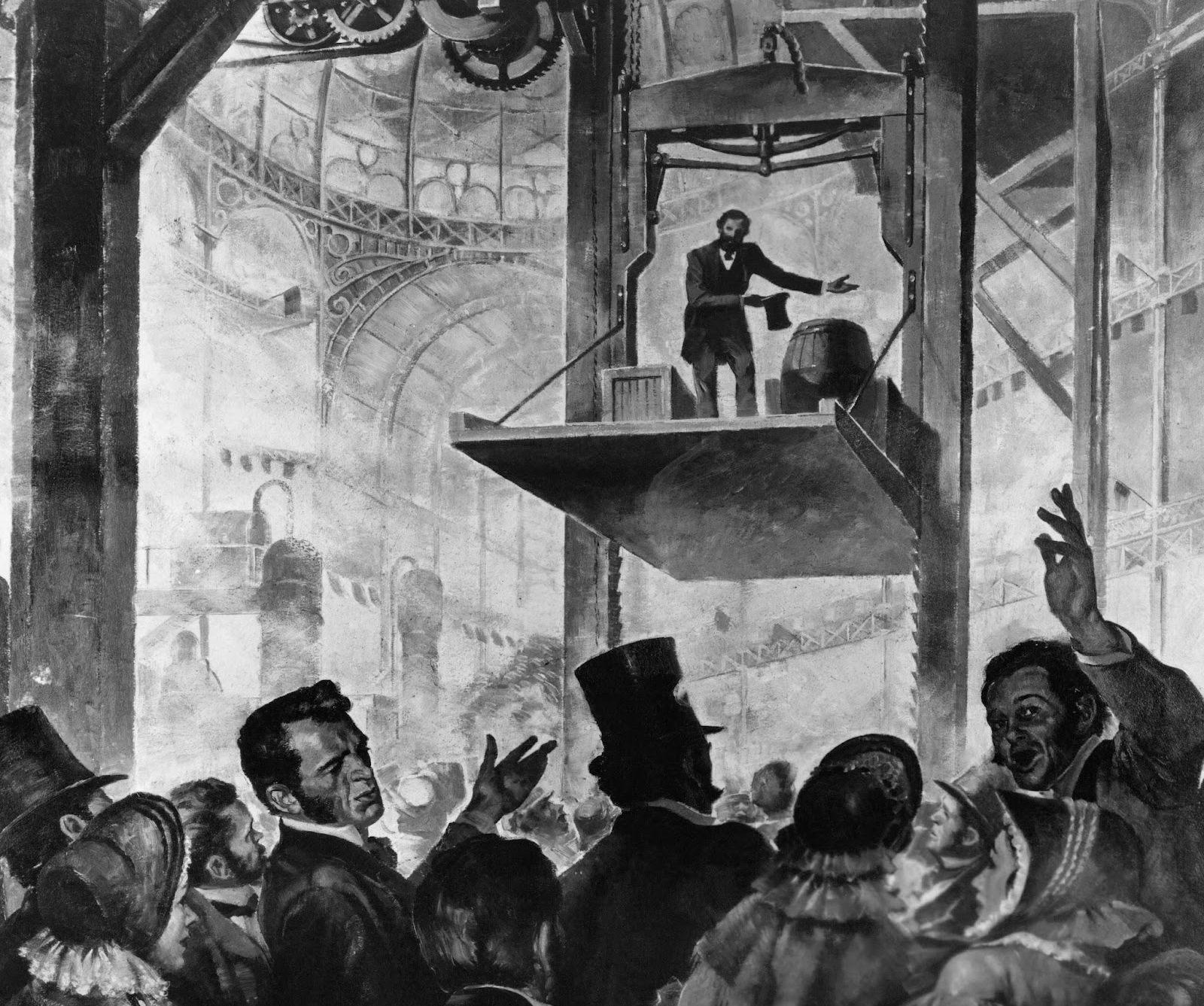

Image: Copie de gravure ancienne, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The New York skyline would look very different today had it not been for the invention of the elevator. The man responsible for the forerunner of the modern elevator was American industrialist Elisha Graves Otis , who, on January 15, 1861, received the first U.S. patent for a safety-type passenger elevator.
The concept of vertical travel was not new. However, the first successful passenger safety elevator was installed in 1857 by Otis in the E. V. Haughwout & Company building, a department store in Manhattan. Otis also held patents for other inventions, including railroad trucks and brakes, a steam plow, and a bake oven. But it was the elevator with its safety feature that brought him fame and his sons great fortune.
6
Lock (Patent #31,278)

Image: Parastoo Maleki
The idea of the lock probably stems from the time man first acquired goods he wanted to safeguard from others. However, the first commercially successful modern lock and key system was invented by American mechanical engineer and metalsmith Linus Yale Jr., who received a U.S. patent in 1861.
Yale developed several types of locks, including the Yale Double Treasury Bank Lock, created at the request of the U.S. government. These designs brought him nationwide recognition, but the invention that made him truly famous was the pin-tumbler cylinder lock . Yale died just a few years after receiving his patent. However, every lock and key produced by the Yale & Towne Lock Company since then has proudly carried the Yale name.
7
Barbed wire (Patent #157,124)

Image: Lexis Chadwick
In an age of video surveillance, barbed wire might seem obsolete. Yet it was crucial to the settlement of the American plains in the late 19th century—and it remains widely used around the world today .
On November 24, 1874, Joseph F. Glidden, a farmer from Illinois, received a U.S. patent for the first commercially successful barbed wire . While several earlier patents had been granted for wire fencing, it was Glidden’s design that proved durable, affordable, and easy to mass-produce—making it the dominant form of fencing on the frontier**.**
8
Air conditioner (Patent #808,897)

Image: Prasopchok
On those hot and humid days of summer, we should all be thankful for the work of Willis Haviland Carrier, often called the father of air conditioning. For his efforts, he received the first U.S. patent for a modern air conditioning system on January 2, 1906.
Air conditioning is a complex process that involves refrigeration, dehumidification, air purification, and circulation. Before Carrier’s invention, various individuals had worked on these individual components. But it was Carrier, an American engineer, who successfully integrated them —focusing on the crucial relationship between temperature and humidity.
9
Airplane (Patent #821,393)
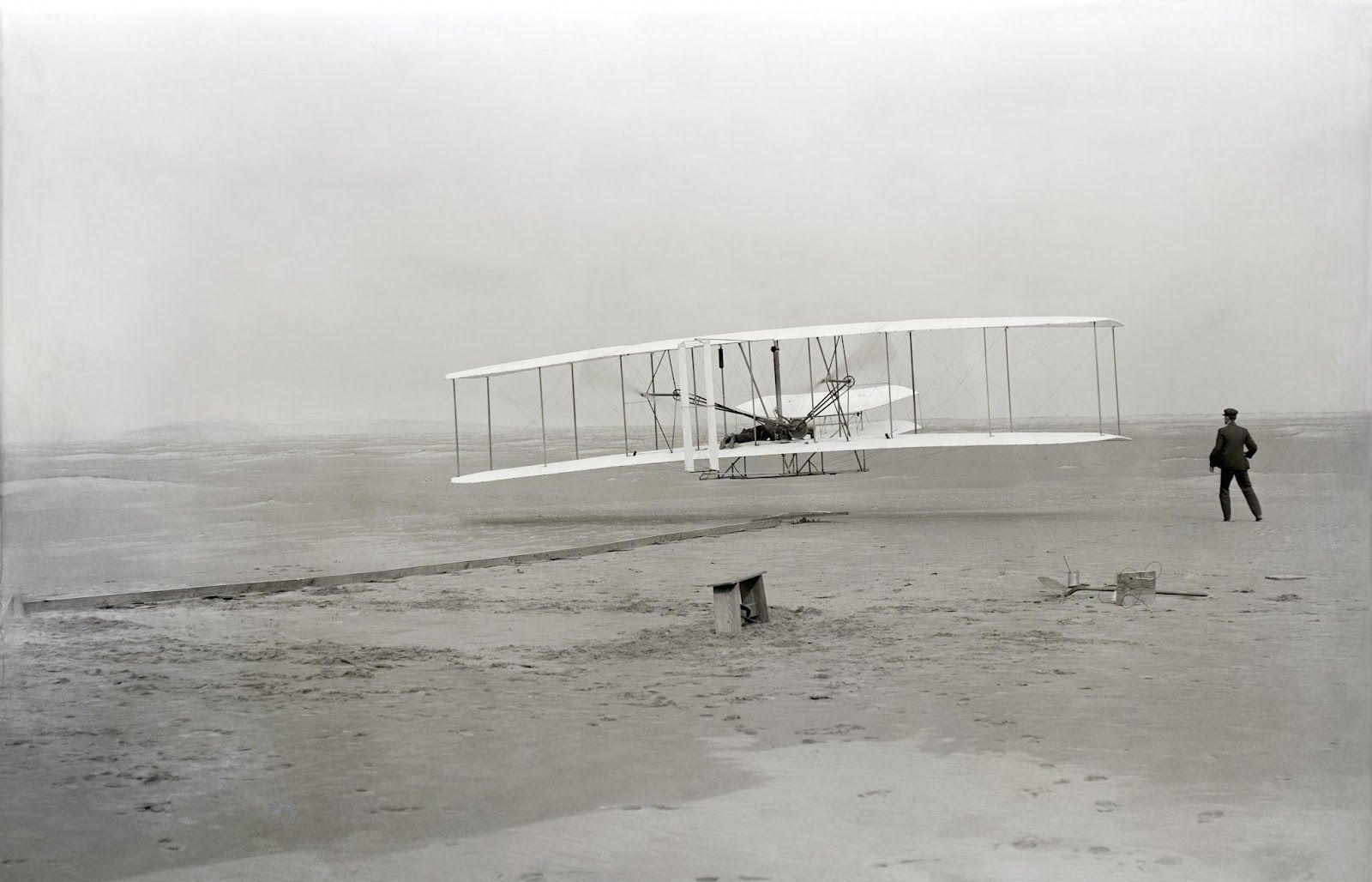

Image: John T. Daniels, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Orville and Wilbur Wright are credited with achieving the first controlled, manned flight in history. For their pioneering work, they received the first U.S. patent for an airplane, issued on May 22, 1906.
Many had been intrigued by the idea of human flight before them. However, it was the Wright brothers who succeeded in building, flying, and promoting the world's first successful airplane —an invention that revolutionized transportation.
10
Bakelite (Patent #942,809)

Image: Call Me Fred
The modern plastics industry wouldn’t exist without Belgian-American chemist Leo Hendrik Baekeland , who received the first U.S. patent for a thermosetting plastic in 1909. Before him, others had attempted to produce synthetic resins but were unsuccessful.
Baekeland corrected his predecessors’ mistakes. The result was the first thermosetting resin —one that, once set, would not soften under heat. Bakelite was the first in a long series of resins that shaped the U.S. economy, paving the way for materials such as cellophane, acetate, vinyl, Plexiglas, acrylic, Formica, and polyester.
11
Frozen food (Patent #1,773,080)

Image: United States Patent Office (Clarence Birdseye, inventor)., Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Do you know where the name Birds Eye Frozen Food comes from? From its inventor! In 1930, American entrepreneur Clarence Birdseye received the first U.S. patent for this type of product.
Food preservation has been a concern since the beginning of time. Techniques such as salting, pickling, smoking, curing, canning, and later inventions like the icebox and home refrigerator have all contributed to preserving food.
However, one of the most successful methods was developed and commercialized by Birdseye. His process involved quick-freezing meat, seafood, vegetables, and fruit in convenient packages without altering their original taste. Birdseye’s name became a household word, and his innovation created a multibillion-dollar industry.
12
Instant photography (Patent #2,543,181)
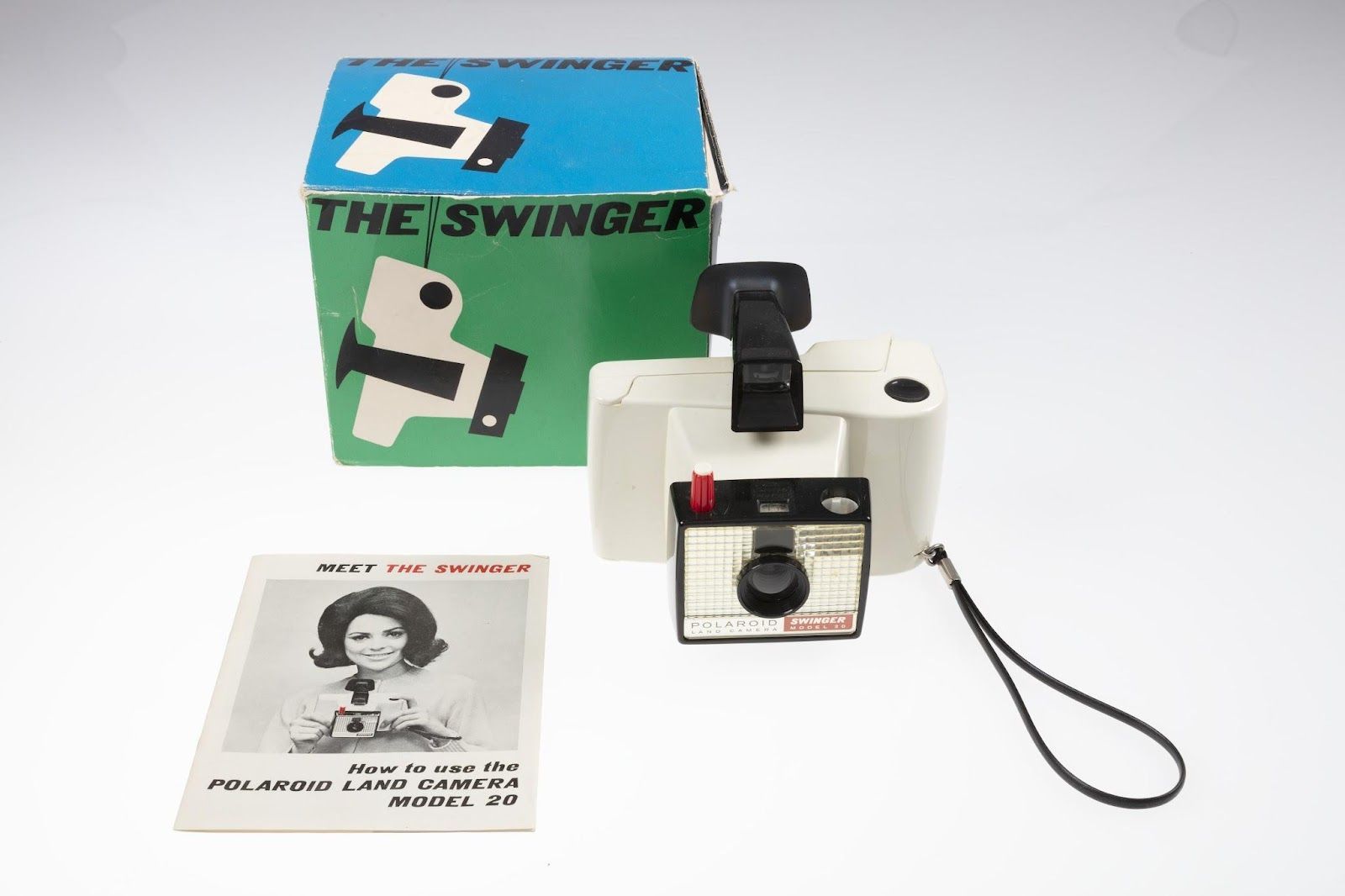

Image: Missouri Historical Society, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
When we think of instant photography, Polaroid is often the first name that comes to mind. But how much do we know about the man behind the company? American scientist, inventor, and co-founder of the Polaroid Corporation, Edwin Herbert Land , was granted the first U.S. patent for a one-step photographic process in 1951.
While on vacation with his family, Land conceived the idea for a camera and film that could produce an immediate photograph. In 1948, the first Polaroid Land Camera went on sale, though without much public approval. Polaroid continued to improve the Land Camera and, in 1965, introduced the affordable Swinger model , which became an immediate success. Throughout his life, Land was granted more than 533 patents, was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame, and received the Presidential Medal of Freedom.



























